No Code Automation Testing
Learn how to create and run automated tests without writing any code using AgentQ's No Code Automation Testing feature.
Prerequisites
- AgentQ account
- Test cases already created (either manually or through AI)
Steps
1. Start No Code Automation
Begin by clicking the "Automation" or "No Code by AgentQ" button in the interface.
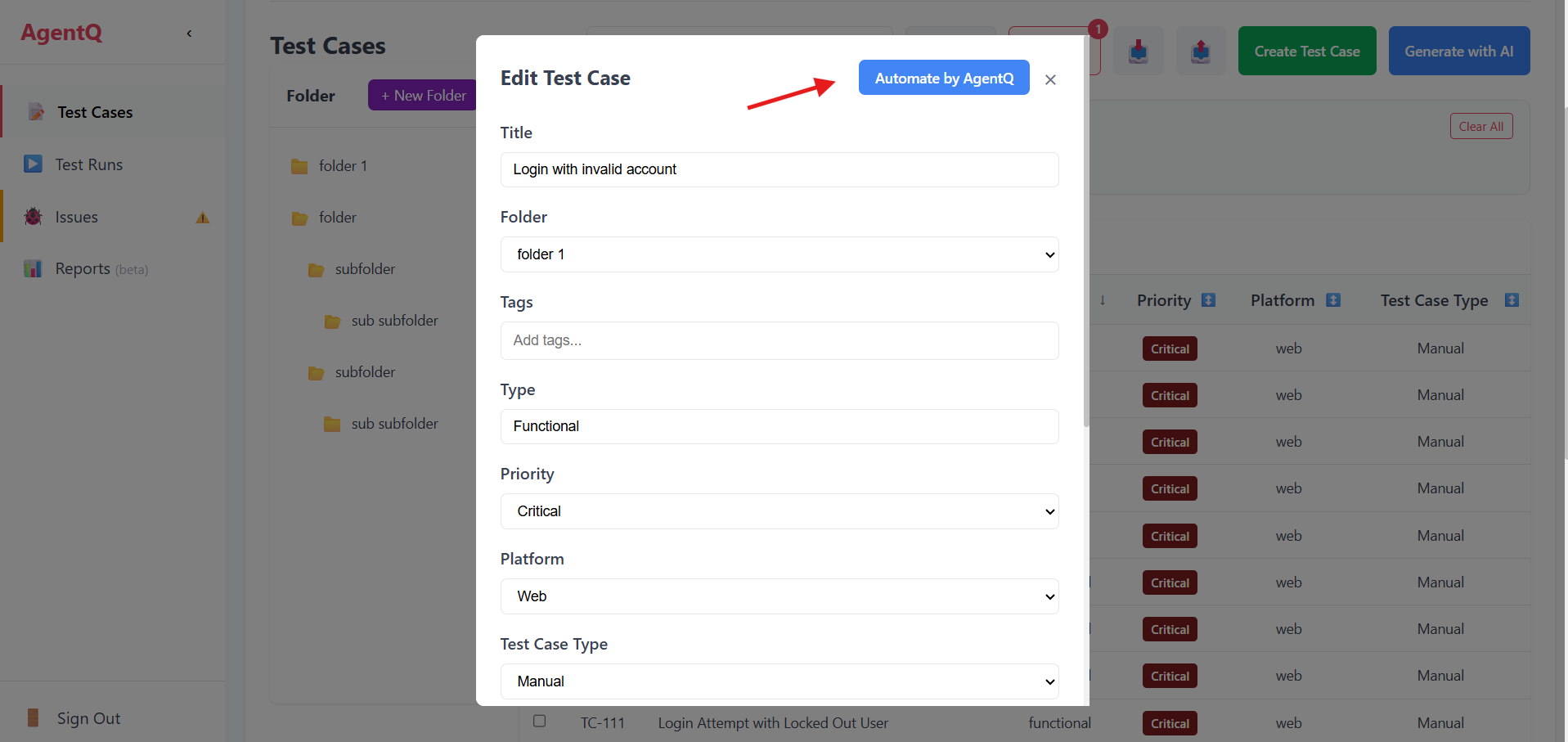
2. Select Test Case
Choose the test case you want to automate from your existing test cases.
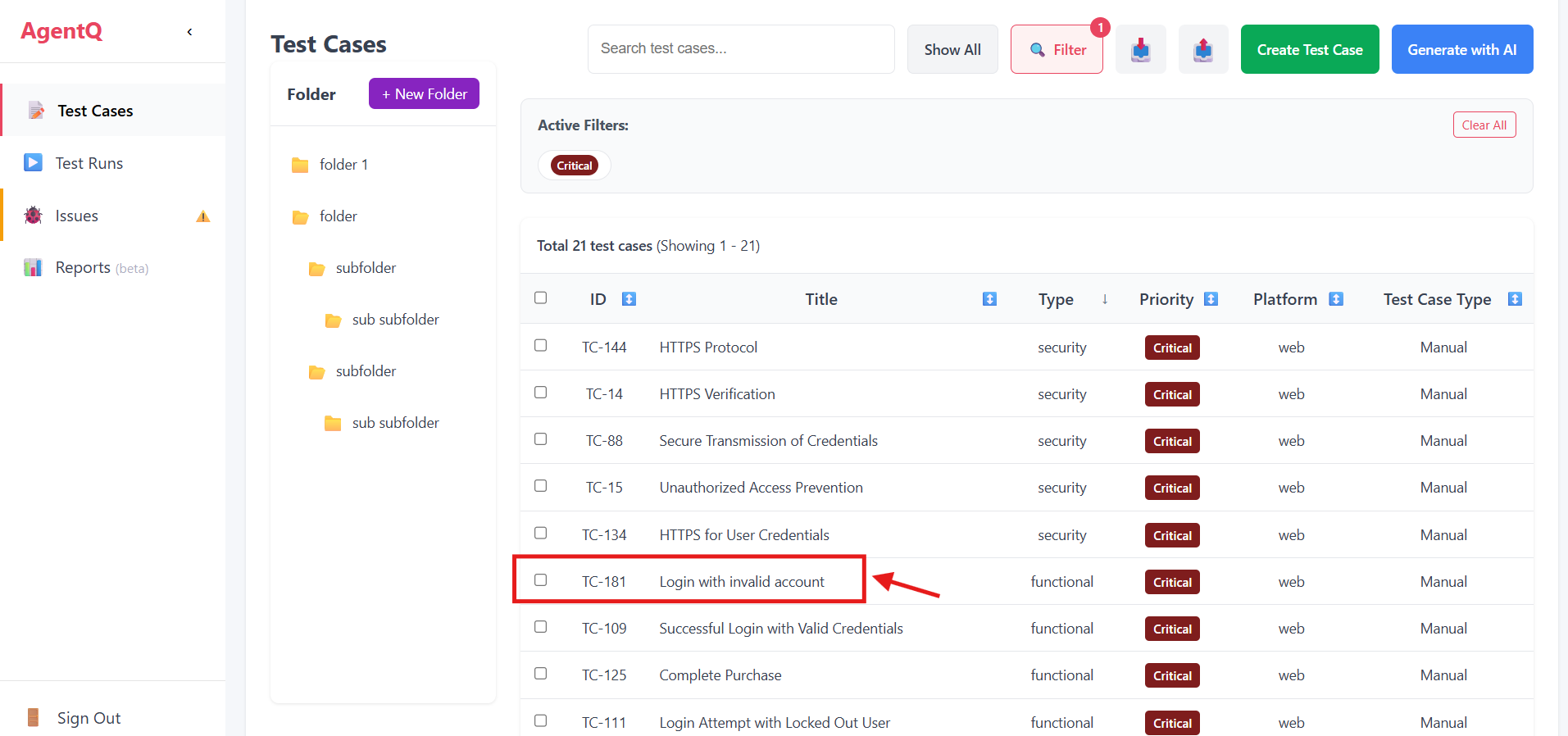
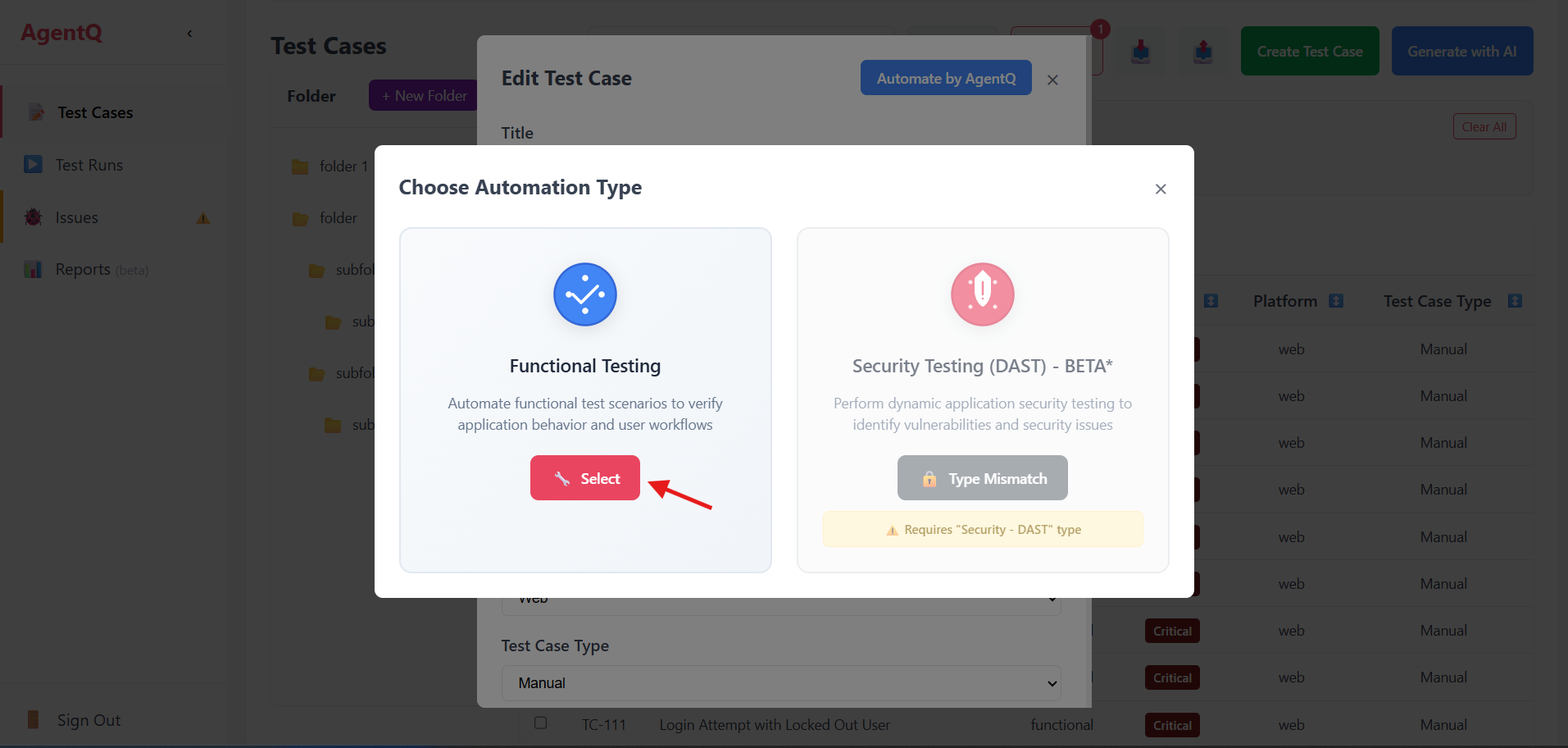
3. Select Testing Type
Choose "Functional Testing" from the available testing options.
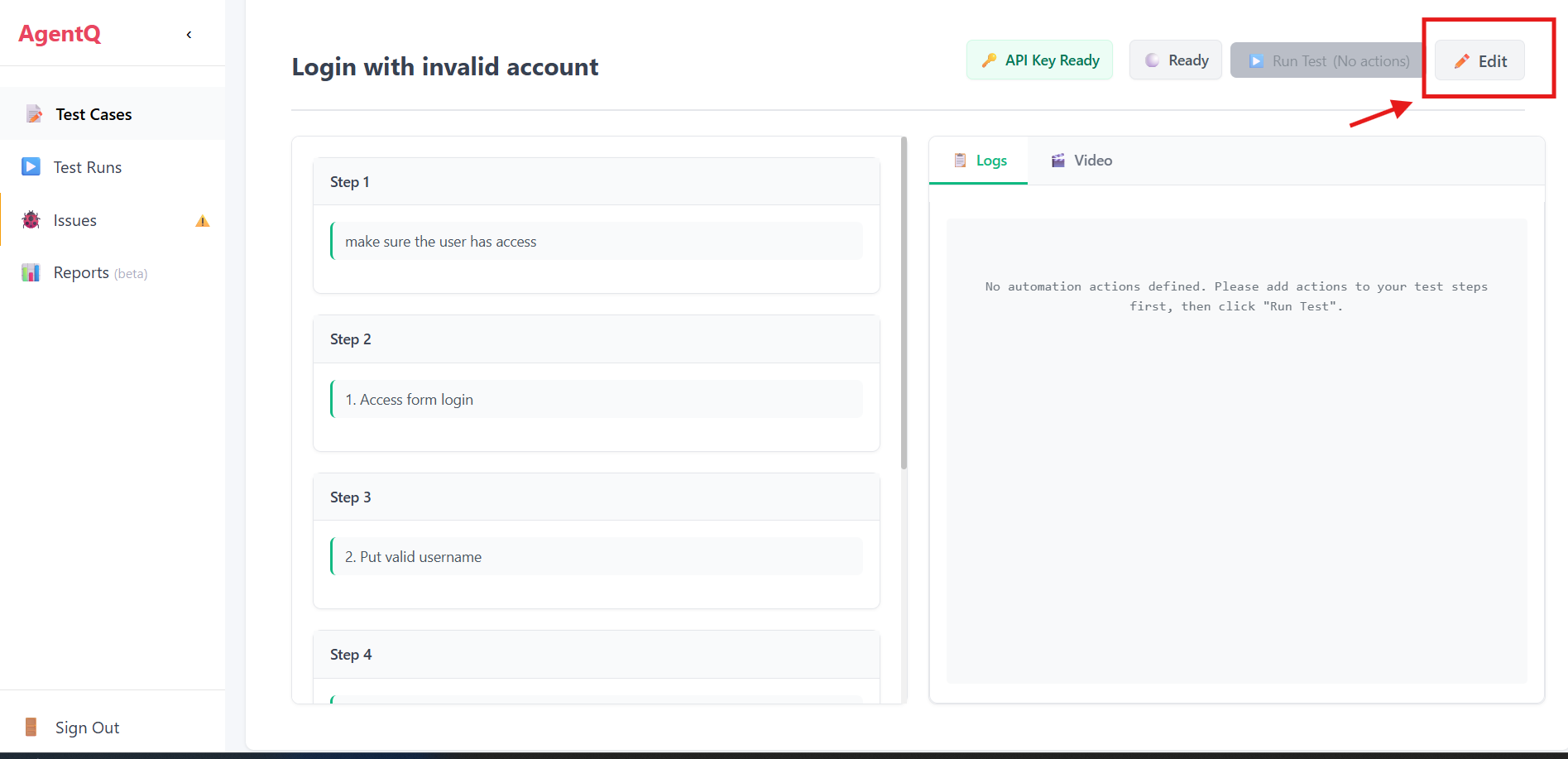
4. Add Interactions
Click the edit button to add commands and interactions for your test automation.
5. Configure Test Steps
In the edit view, add prompts or interactions that define how the test should be executed. This is where you specify the actions that should be performed during the test.
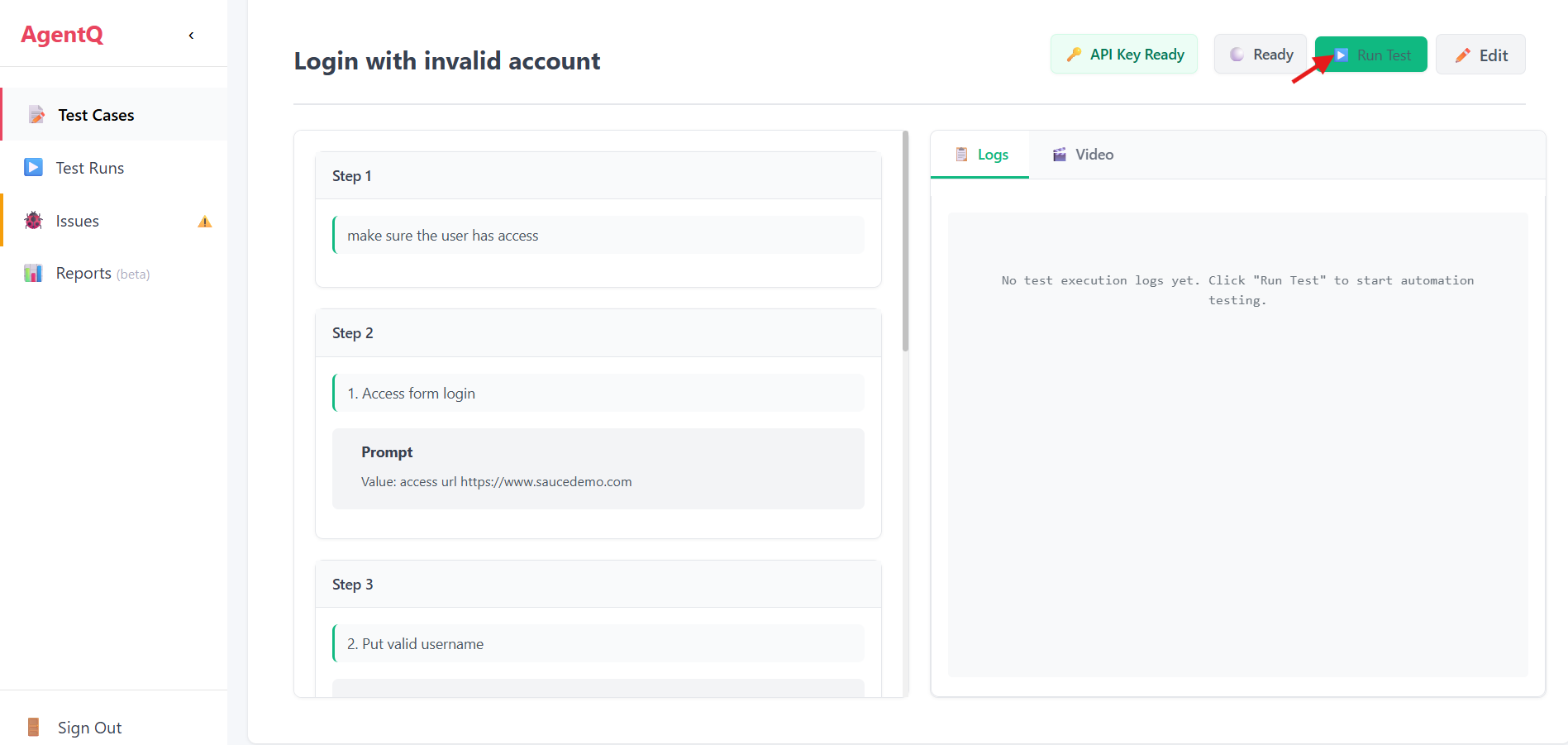
6. Run the Test
Once you've configured all the interactions, click the "Run Test" button to execute your automation.
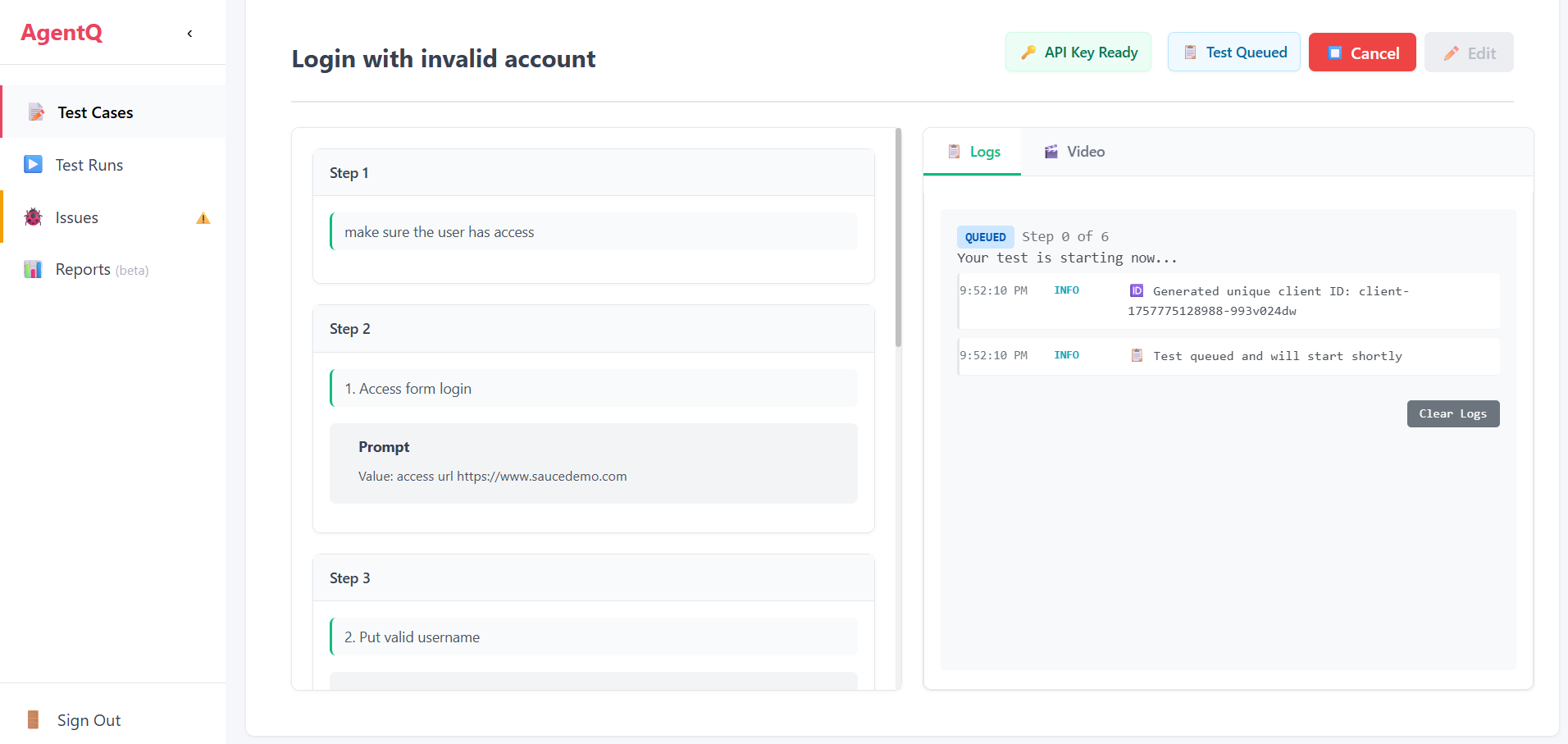
7. Test Execution
The system will begin executing your automated test case. You can monitor the progress during this phase.
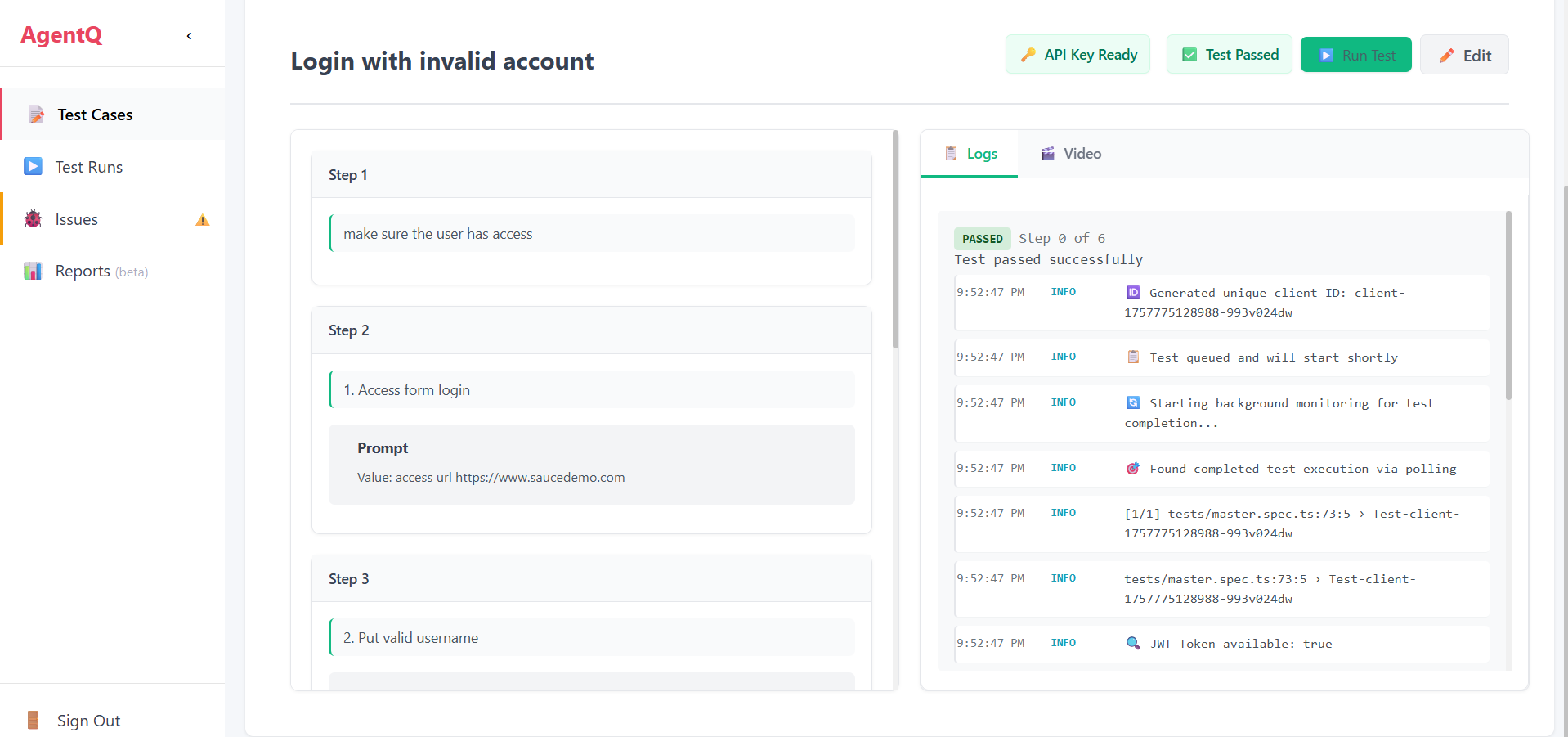
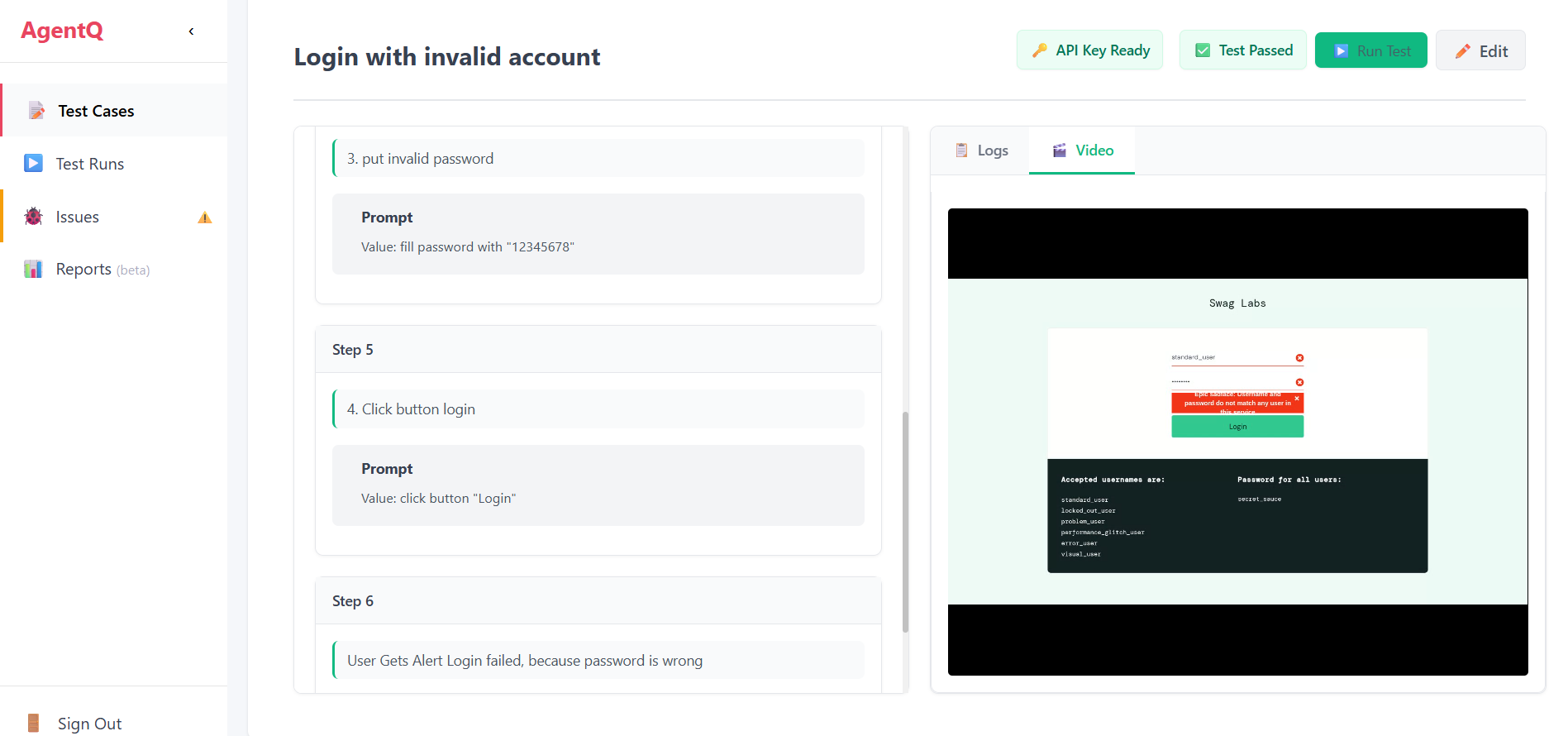
8. View Results
After completion, you can view the test results:
- Check the test status (Pass/Fail)
- Review video evidence of the test execution
Tips
- Start with simple test cases when learning the no-code automation feature
- Be specific and clear when defining interactions
- Review the generated video evidence to understand test execution
- Use descriptive names for your test cases and interactions
- Make sure all necessary test data is prepared before running automation
- Regularly review and update your automated tests to maintain reliability
Best Practices
-
Test Planning
- Plan your test scenarios thoroughly before automation
- Identify critical paths that need frequent testing
- Consider edge cases and error scenarios
-
Interaction Design
- Keep interactions simple and focused
- Use clear, descriptive commands
- Verify each step works before adding the next
-
Maintenance
- Regularly review and update automated tests
- Document any special conditions or requirements
- Keep track of successful and failed executions